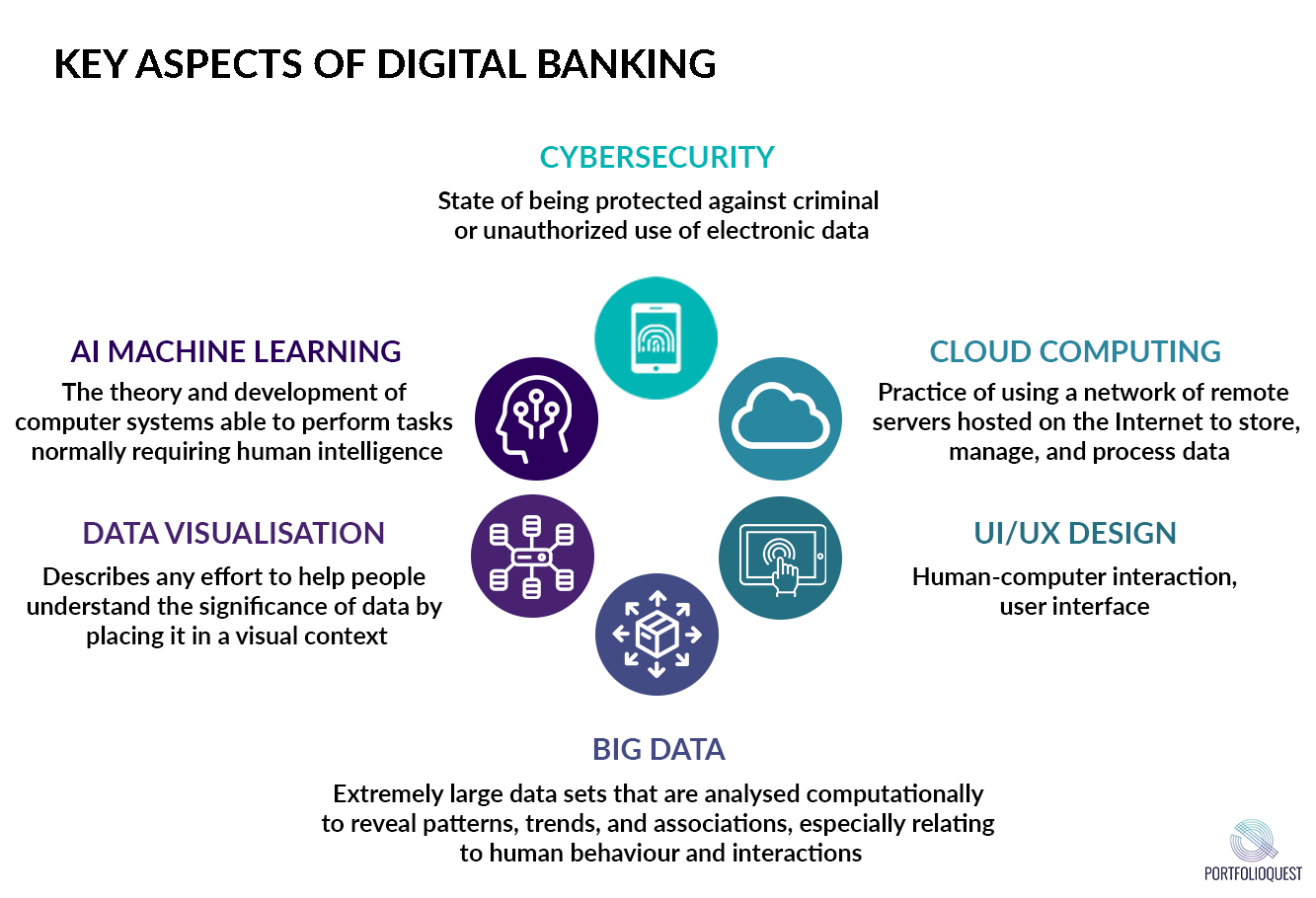
Previously, we showed you the differences between a traditional and digital bank as well as the new skills needed. We concluded that having an open and forward-thinking mindset will make you a valuable player in the digital transformation.
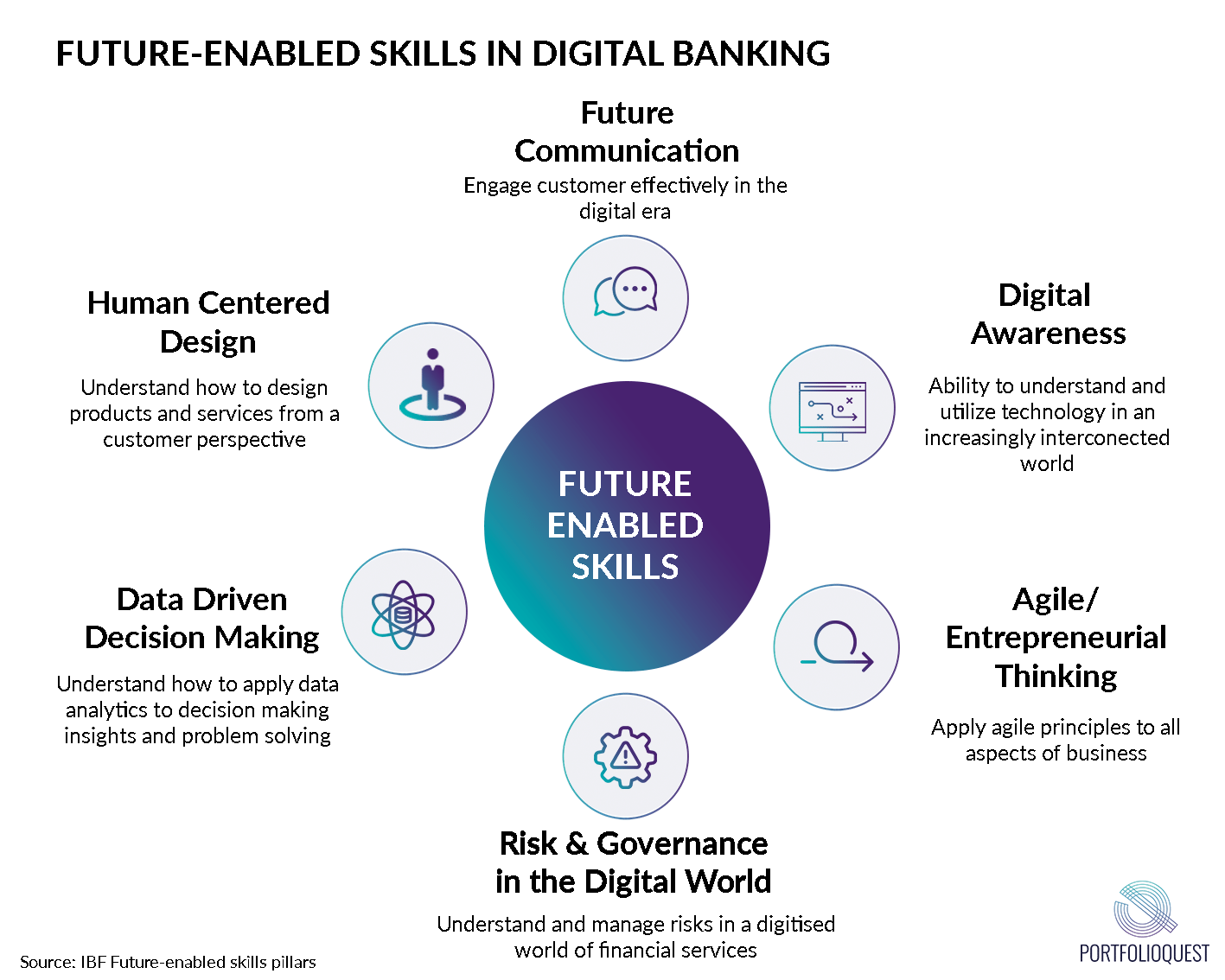
In this article, we will explore greater into detail about the types of skills needed in the digital banking landscape. Inspired by IBF’s future-enabled skills pillars, the six skills reflect the importance of being tech savvy and having a good understanding about the business.
With the digital transformation well underway, there is a need to rethink talent. Banking professionals are no longer expected to possess technical skills but rather are increasingly required to be tech savvy. Banks are redefining job roles and restructuring their organizations to facilitate various digital banking initiatives. According to Cognizant, this has become so important that failure to do so will cause banks to risk losing their training investments as newly skilled employees leave for other opportunities. Coupled with the need for a dramatic cultural change for the digital transformation, having these digital skill sets will set you apart from the rest.
- Future Communication
With the decline of branch locations and increasing adoption of mobile banking, being able to engage effectively with customers is key. According to Accenture, 66% of customers execute half of their banking transactions online, and 71% are open to automated support. Deloitte notes that mobile banking is slowly becoming popular and a focal point in the banking experience. Consumers of mobile banking demand improvements in basic functions such as opening accounts and seeking support. Being able to engage consumers through digital channels would allow banks to better map the customer journeys, offer personalized offers and products. According to Accenture, future ready banks are already incorporating advanced Know Your Customer (KYC) and multifactor authentication approaches into their digital apps for continued engagement.
- Digital Awareness
Having a basic understanding of the major aspects of digital banking and how they can be applied to the business is important. In the increasingly connected world, digital platforms are becoming the preferred channel to reach customers. Digital marketing and sales are key points that deliver digital banking services. According to Accenture, artificial intelligence is used to provide contextual, holistic advice in the form of chatbots. Such channels are adopted in the customers’ best interest, which will likely promote brand loyalty. Although retail banking will remain personal to a large extent, there is still a need to integrate digital know-hows. With the application of new technologies in banking, it will be important to get familiar with the tools in terms of where they are going in the short term and their long-term potentials.
- Agile/Entrepreneurial Thinking
As mentioned in the previous article, having an open and adaptable mindset is key. This is especially important in agile organizations where change is the only constant. Deloitte notes that the core objectives for most banks is to achieve organizational agility, which encourages innovation and upskilling of talent to meet the needs of the ecosystem. A recent Accenture study notes that full-service retail banks could lose as much as 35% of their market share by 2020 if they are not agile. With digital disruptors offering better quality products and services, non-agile banks are facing strong competition. The adoption of digital technologies such as mobile applications, social media and data analytics allows banks to build the agile mindset to remain competitive in the future.
- Risk & Governance in the Digital World
In the digitized world of financial services, new kinds of risks are abundant. Risks associated with synthetic identity fraud, cybersecurity and regulatory compliance could potentially threaten bank’s control over customer experience. Increasingly, banks will need to improve on differentiating real from fake customers with the use of digital platforms. The potential for cyber risk has also been increasing with the greater interconnectedness and utilization of new technologies in the banking ecosystem. Most importantly, unmet regulatory expectations could potentially put banks at risks in terms of compliance functions. It is therefore important for one to be able to understand and manage such risks in the process of digitalization.
- Data-Driven Decision Making
In the previous article of FinTech trends and how it impacts your career, we talked about how integrating data was a key to help propel the digital banking transformation. Data analytics is heavily used in banks for decision making and problem-solving. A data-driven approach to customer segmentation allows banks to deliver targeted messages to the right audience. Also,real-time data allows banks to be more agile and reduce costs in response to abrupt changes. DBS DigiBank’s budget optimizer uses data about customers’ behaviors and provides recommendations based on that. Data skill sets are important to generate insights and deliver better customer experience.
- Human Centred Design
Digital banking focuses on customer centricity and delivering seamless customer experience through different channels. Such an approach requires that banks design products and services from a customer perspective. When banks incorporate the customer in the design process to fit the needs of that customer, the products and services hold more value to the customer. An example of this can be seen in DBS DigiBank’s AI-driven virtual assistant that can hold “human-like” conversations. Customers are able to feel heard and understood as the virtual assistant could anticipate and answer some 1,000 customer questions. Given that new technologies are influential in banks, preserving the human element will become important when designing useful products for customers.
For a bank to succeed in the technology-driven world, technical talent is important. However, there is also a need to value enduring human skills for a bank to succeed in the long run. Upskilling and retraining are key for current and future bankers to work more effectively in a digital environment.
In the next article, we will explore where you can obtain such skills. Stay tuned for that!